AIX-Net-WWR, the Aachen network for wastewater reuse, has been launched
AIX-Net-WWR, the "Aachen Network for Waste Water Reuse", is a network that wants to "give new life to waste water", not just once but again and again.
After a selection process lasting several years, the Aachen-based entrepreneurial and research network Aix-Net-WWR was able to prevail alongside numerous other applications and started at 1.1.2024 to develop innovative solutions for the reuse of wastewater over the next three years. The approximately €12 million project, which focuses on the Aachen city region, is being funded by the RUBIN ("Regional Entrepreneurial Alliances for Innovation") program under the "Innovation & Structural Change" heading of the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF).
The environment
Around the world, climate change with record heatwaves and droughts is increasingly leading to regional water shortages on the one hand and heavy rainfall events with associated flooding on the other. After many years of intensive negotiations, all United Nations member states have committed to changing the global economy in a climate-friendly way. The GREEN Deal should lead to investments of at least €1 trillion in the European Union by 2050.
The goals and recommendations for action are described in the United Nations' 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Sustainable water management is a key prerequisite for implementing and achieving a large part of these Sustainable Development Goals.
At the same time, ESG (Environmental Social Governance) investment criteria have become established on the financial market. This shows that only sustainable entrepreneurship can be economically worthwhile in the future.
The new Aix-Net-WWR alliance is based on these pioneering framework conditions.
Current situation and goals
Most cities today have a centralized water supply and wastewater disposal system. However, this has a number of disadvantages, especially in water-scarce regions, such as decreasing water supplies with increasing water demand and the loss of valuable materials, especially in the form of water and heat (approx. 55 m³ water/person/year and approx. 550 kWh/person/year) for direct recycling at the point of wastewater generation.
In many central sewage treatment plants, the wastewater is also insufficiently treated for possible reuse, depending on the size of the connection, so that the remaining substances contribute to increasing water pollution.
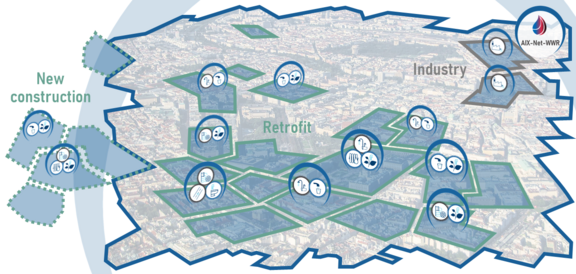
In the Aix-Net-WWR city of the future, there should be standardized, semi-decentralized wastewater reuse systems at district level with innovative individual technologies that address the problems mentioned. Semi-decentralized means that several buildings are connected to one system. The advantages of semi-decentralized systems lie in particular in the close spatial linking of wastewater generation and treatment. This enables the direct reuse and utilization of the treated water and the energy present in the wastewater directly at the place where the wastewater is generated, and this is optimized both ecologically and economically.
AIX-Net-WWR has set itself the following goals for the design of the semi-decentralized processing systems:
the possibility of treating wastewater to produce different water qualities, such as bathing water, irrigation water, process water, hygiene water and drinking water
the use of the systems in the construction of new residential areas, but also for retrofitting existing structures with the involvement of local supply and disposal companies
a modular and scalable structure and
the economic efficiency of the systems within a few years through enormous savings in the core resources of water and energy.
The innovative individual technologies within the standardized systems should also be able to treat industrial and commercial wastewater, thus enabling individualized solution models.
The implementation
To make this vision possible, the following innovative water treatment technologies are to be researched and developed in five joint projects as part of the implementation phase:
In the 1st joint project, AIX-WWR, a complete demonstrator in container form is being developed for the treatment of domestic wastewater with the aim of achieving the most complete recirculation possible. A core component of this demonstrator is an innovative, energy-efficient membrane bioreactor, which is being adapted to the special requirements of semi-decentralized plants as part of the joint project. The demonstrator will treat 20 m³ (equivalent to approx. 135 PE) of domestic wastewater. For this purpose, it will be installed, tested and further developed locally during the project period.
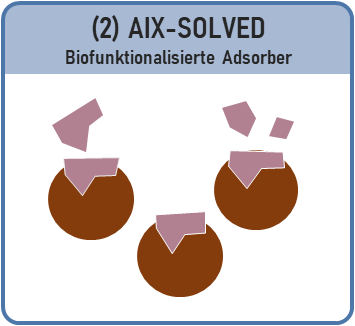
In the second joint project - AIX-SOLVED - a purification process is being developed in which adsorber granulate is biofunctionalized with enzymes. The aim is for enzymes - i.e. biological material - to adhere to a new type of granulate and, together with the granulate, remove impurities from the water.
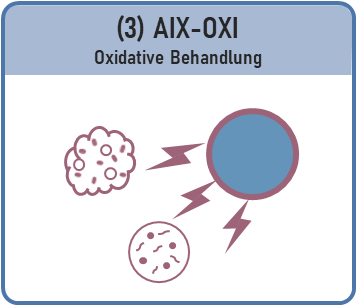
In the 3rd joint project - AIX OXI - a new type of plasma reactor is being developed for the first time in order to achieve energy-efficient removal of trace substances and disinfection of water. This involves splitting air molecules into ions and electrons which, when introduced into the water, break down organic impurities.
The 4th joint project - AIX-WATCH - focuses on the central issue of ensuring the quality and hygienic safety of the treated wastewater. To this end, a new validation methodology is to be developed using innovative monitoring and control concepts.
The 5th joint project - AIX-DEZI - is concerned with the decentralized treatment of industrial wastewater streams containing salt, heavy metals or trace substances using innovative nanofiltration membranes and a new type of FCDI deionization - a desalination process in flow-through operation - as completely as possible and enabling reuse in the process.
The alliance management:
Alliance Coordinator and Public Relations: Oliver Ringelstein INTEWA GmbH
Scientific spokesperson & infrastructure: Prof. Dr. Thomas Wintgens, ISA RWTH
Coordination Research & Development: Prof. D. Arnold Gillner, ILT Fraunhofer
Marketing & Sales: Dr. Süleyman Yüce, STEP Consulting GmbH
Finance & Controlling: Johanna Kunsmann, CON RWTH
Table 1: AIX-NET-WWR alliance partners
Company / Institution | Core competence | Website | |
| 1 | INTEWA GmbH | Water treatment and rainwater management | www.intewa.com |
| 2 | Aixprocess GmbH | Simulation technology, big data applications and real-time process optimization | www.aixprocess.de/ |
| 3 | Hego Biotec GmbH | Active substances for environmental protection, substances for wastewater and sludge treatment | www.hego-biotec.de/ |
| 4 | Prüfinstitut für Abwassertechnik GmbH | Accredited and notified testing body for decentralized, wastewater technical systems | www.pia-gmbh.com |
| 5 | SeSaM-Biotech GmbH | Discovery, development and production of enzymes (protein engineering) | www.sesam-biotech.com |
| 6 | STEP Consulting GmbH | Planning and implementation of process and energy technology projects for (waste) water purification and desalination | www.stepconsulting.de |
| 7 | SV Steuerungstechnik GmbH & Co. KG | Electropneumatic controls, programming and visualization for technical systems | www.sv-steuerungstechnik.de |
| 8 | SIMA-tec GmbH | Development of laboratory and pilot plants for R&D services in process and wastewater technology | www.sima-tec.de |
| 9 | Redline Technologies Elektronik GmbH | Development of process power supplies for industrial and medical applications | www.de.redline-technologies.de |
| 10 | nrw-Anlagentechnik GmbH | Development and production of screening systems, fine screens and screw separators | www.nrw-anlagentechnik.de |
| 11 | Bühler Technologies GmbH | Development and production of inline sensors for real-time monitoring of gases and fluids | www.buehler-technologies.com |
| 12 | Ruhr-Universität Bochum | Working Group for Biomedical Applied Plasma Technology (BPT) / Chair of Applied Electrodynamics and Plasma Technology (AEPT): Experimental implementation and diagnostics of various technical plasma processes | www.ruhr-uni-bochum.de |
| 13 | DWI – Leibniz-Institut für Interaktive Materialien e.V | Membrane processes, development and modification as well as process development | www.dwi.rwth-aachen.de |
| 14 | Forschungsinstitut für Wasserwirtschaft und Klimazukunft an der RWTH Aachen e. V. | Optimization of wastewater disposal, energy generation at wastewater treatment plants, online analytics | www.fiw.rwth-aachen.de |
15
| Fraunhofer Aachen | Institute for Laser Technology (ILT): New laser beam sources and processes for materials processing, metrology and life sciences | www.aachen.fraunhofer.de |
Institute of Molecular Biology and Applied Ecology (IME): Development of biotechnological production platforms for peptides, proteins and enzymes | |||
| 16 | Rheinisch-Westfälische Technische Hochschule Aachen | Institute for Sanitary Engineering (ISA): Water recycling use, trace substance elimination, membrane applications, environmental analysis | www.rwth-aachen.de |
Chair of Biotechnology (ABBT): Protein engineering with evolutionary and rational methods | |||
Chair of Controlling (CON): Environmental, business model, innovation, transformation and value creation controlling | |||
17
| Korallenwächter – Kowalytics UG | Hardware and software for recording and evaluating measurement data (titration and colorimetric methods) | www.kowalytics.com |
Aix-Net-WWR is also supported by numerous stakeholders, such as industrial companies and, above all, water suppliers and disposal companies, as well as other organizations from the construction and environmental sectors.
The management consultancy Isle Utilities, which specializes in municipal supply and disposal companies, has calculated the market potential for Aix-Net-WWR at a total of € 100 billion for the year 2031. By 2031, the alliance plans to hire 200 additional employees from the region to work on implementing the targets set. Da s alliance is open to further associated partners who wish to actively support the project. The common goal is to make Aix-Net-WWR a leading global network for water reuse and to give wastewater a new lease of life.
Characters: 11,242 (incl. spaces)
Alliance coordinator: INTEWA GmbH
Authors: Oliver Ringelstein, INTEWA GmbH
E-Mail: aixnetwwr@~@intewa.de